Why Your Modem and Router Lights Are Blinking
Find out what all those lights on your modem and router actually mean and how to use them
Dec 8, 2025 | Share
Equipment Guides
The LEDs on your modem, optical network terminal (ONT), router, or modem/router combo (gateway) are most likely blinking because they’re communicating what the device is doing, or there’s an error.
All networking devices, like modems and routers, provide a row of status lights that represent the essential functions of two networks: Your provider’s network and your home network. These functions are similar across most routers, modems, ONTs, and gateways, though they’re often labeled differently based on the manufacturer.
Read on to learn what the lights represent, what different colors mean, and how to use this information to diagnose and solve home networking woes.
Tired of troubleshooting your internet?
Maybe it’s time for a new internet provider. Enter your zip code to see what’s available in your area.
In this guide:
Understanding blinking lights | Understanding light colors | Understanding light meanings | Easy fixes for modems, ONTs routers, and gateways | FAQ
In this guide:
Blinking lights on a router, modem, or gateway
All modems, ONTs, routers, and gateways use blinking lights to indicate processes, data transmissions, and sometimes errors.
Slow and steady blinking
A light blinking slowly and steadily typically indicates the equipment is attempting to establish a connection. For example, when you power up a modem or gateway, it’s common for each light to blink slowly for a while before staying solid. This represents the process of establishing whatever connection is represented by the light.
If a light doesn’t stop blinking slowly and steadily after a long time, say 20 minutes, that’s usually a sign there’s an issue with that process. For example, if a modem’s upstream light continues to blink slowly for over 20 minutes, that typically means it can’t establish a connection to the internet.
Rapid blinking
Sporadic, rapid blinking is usually nothing to worry about. It’s often used in Wi-Fi and Ethernet lights to represent the transmission of data. It just means those functions are in use and working correctly.
What do light colors mean on your router or modem?
Colors can vary across different brands and models of modems, ONTs, routers, and gateways. Sometimes, the different colored lights are used to represent different states of functionality.
Green and white
Green or white colored lights usually indicate things are functioning normally. But some models always maintain green or white colored lights and use blinking to signify different states.
Yellow
Yellow lights represent processes, such as booting up or updating, and issues with wired connections.
Red or orange
Red or orange lights usually indicate a problem or error with your modem, ONT, router, or gateway.
Blue
In some cases, a blue LED means the device is ready to set up via Bluetooth. In other cases, a solid blue light indicates that the modem or gateway is connected to the internet—a blinking blue light indicates that it’s trying to connect. Some devices only use blue LEDs, so the function and status squarely depends on the label printed next to them.
Understanding the lights and symbols on modems, ONTs, routers, and gateways
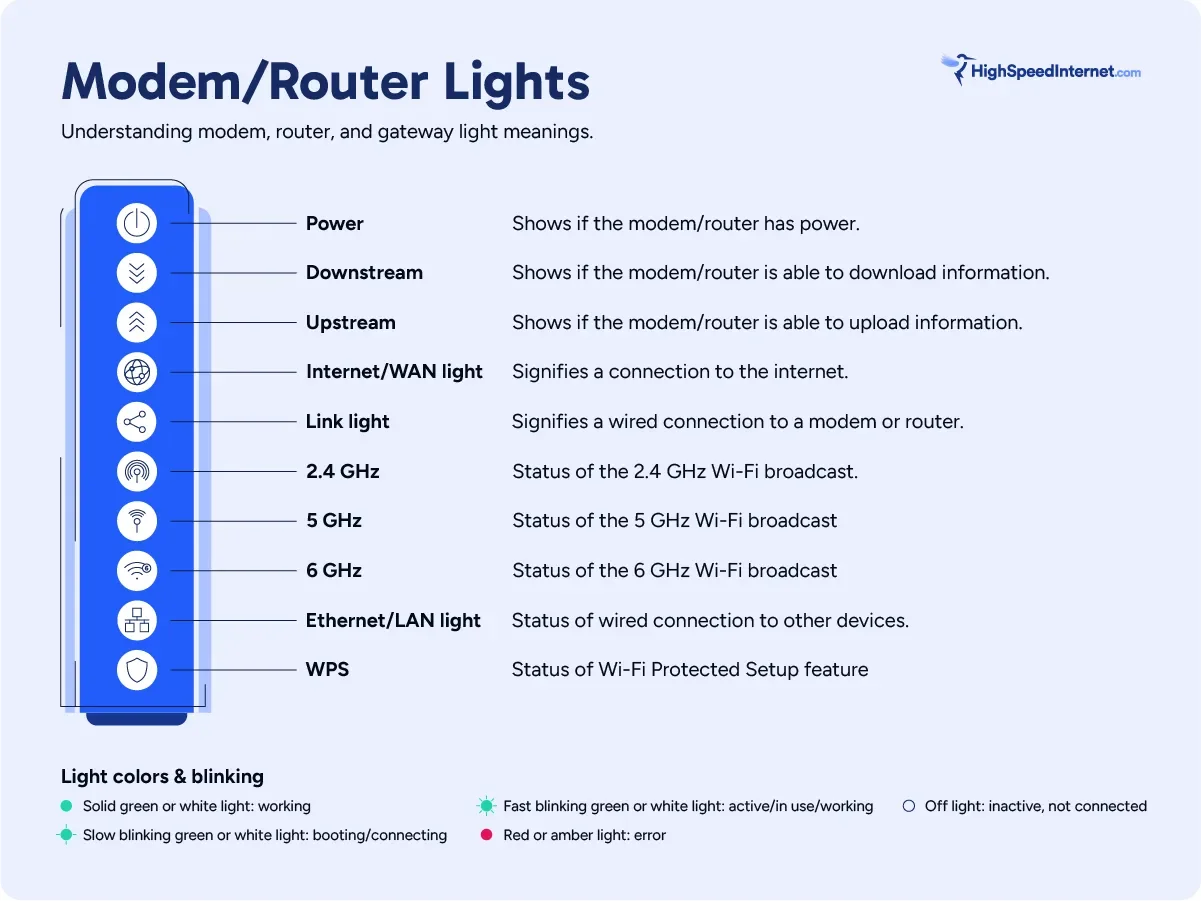
Symbols are mostly used on gateways and routers. If no symbol is present, then you’ll see a label printed next to the LED, like Power or Alarm. Here’s a generalized list of symbols and their associated labels and LED colors.
 Power
Power
Device: All
Color: Green
Usually the first light in a row or column, the power light signifies that the modem, ONT, router, or gateway is turned on and has power. The power light is usually solid but may blink when the equipment is booting up.
 Downstream data
Downstream data
Device: Cable modem, DSL modem, Gateway
Color: Green
Labeled with a down arrow or DS, the downstream light indicates a modem or gateway’s ability to receive information from the internet. This light will blink slowly as the equipment boots up and quickly as you download data. Depending on the model of your equipment, the downstream light may also stay solid.
If your downstream light is red or off, you may not be connected to the internet. Typically, a rapidly blinking light means your connection is working and transmitting data, but this can vary for different manufacturers.
 Upstream data
Upstream data
Device: Cable modem, DSL modem, Gateway
Color: Green
Following the downstream light, the upstream light indicates your modem or gateway is able to send information to the internet. Like the downstream light, the upstream light will blink slowly as your equipment boots up. When operating normally, the upstream light will either blink quickly and sporadically or stay solid.
Some networking equipment uses a single light to represent both the upstream and downstream functions.
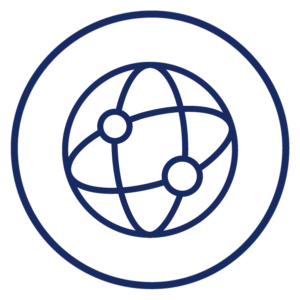 Internet / WAN / PON
Internet / WAN / PON
Device: All
Color: Green, yellow
The internet light, also sometimes labeled WAN or PON (fiber only) or with a globe icon, signifies a connection to the internet. The internet light usually appears right after the upstream data light on modems.
The internet light should be solid green or white when the equipment is functioning normally. If the light is red or off, there’s a problem with your internet connection. It’s normal for the internet light to be blinking during boot up, but if it never goes solid, your equipment is having trouble connecting to the internet.


 Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi
Device: Router, Gateway
Color: Green
Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) is meant to simplify the setup of your home Wi-Fi network and device connections. This feature allows you to skip entering your lengthy passwords every time you add a device—which sounds great in theory, but can pose security risks for unauthorized access to your network.
Most modern routers and gateways have a WPS button you need to press to activate this feature, while some connections happen automatically or are initiated by the device rather than the router itself. A blinking WPS can indicate the router is in pairing mode and ready to connect to devices.
The WPS feature allows devices like security cameras and printers to connect to your router, but disabling this feature if you aren’t actively connecting a device can help protect your home network from unwanted device connections.
How to get the most out of your Wi-Fi
There’s a lot you can do to improve your Wi-Fi speeds. Use these resources to optimize your home’s ces/where-shouldwireless internet.
Step 1: Router placement
Use our router placement guide to help you find the perfect spot to optimize your Wi-Fi signal strength and range.
Step 2: Choose the right Wi-Fi band
Many routers, gateways, and mesh systems now use Smart Connect by default, so you can’t manually switch Wi-Fi networks unless you created separate ones during setup. However, you should have options to choose the preferred connection. Read our guide on how to log into your router for more information about how to access these settings.
Step 3: Run a Speed test
Use our internet speed test to verify your Wi-Fi is running as it should be. You can use your internet plan’s advertised speed as a reference. Just know that wireless speeds are usually slower than connecting via Ethernet.
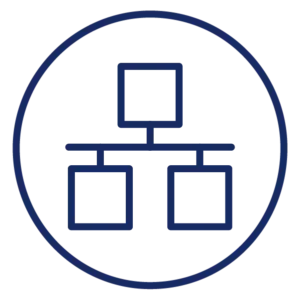 Ethernet / LAN
Ethernet / LAN
Device: Router, Gateway
Color: Green or yellow
The LAN light represents a connection between the router or gateway and a wired device connected via an Ethernet cable, like a computer or game console. The LAN lights may flash or remain solid when in use.
If you have a device connected to your router or gateway via Ethernet and the light is red or off, you have a problem with your Ethernet connection. It could be with the Ethernet port on your router, the Ethernet cable, or the Ethernet port on your device.
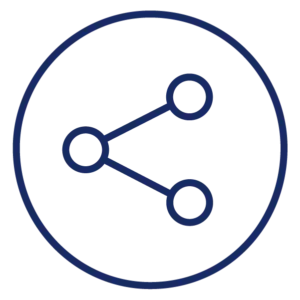 Link / Data
Link / Data
Device: Cable modem, DSL modem, Fiber ONT
Color: Green or yellow
The Link or Data light represents an Ethernet connection between a standalone modem or ONT and a router. It may be solid or flashing when in use.
If you have a separate modem and router, there’s an issue with the connection between your modem and router if the link light is red or off. It could be a bad Ethernet cable or a problem with an Ethernet port.
 Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS)
Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS)
Device: Router, Gateway
Color: Green
The Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) feature on a router is meant to simplify the setup of your home Wi-Fi network and device connections. This feature allows you to skip entering your lengthy passwords every time you add a device—which sounds great in theory, but can pose security risks for unauthorized access to your network.
Some routers have a WPS button you need to press to activate this feature, while some connections happen automatically or are initiated by the device rather than the router itself. A blinking WPS can indicate the router is in pairing mode and ready to connect to devices.
The WPS feature allows devices like security cameras and printers to connect to your router, but disabling this feature if you aren’t actively connecting a device can help protect your home network from unwanted device connections.
Alarm
Device: ONT
C0lor: Red
Normally provided on optical network terminals (ONT), this red light indicates that the unit is not receiving a signal from your fiber internet provider’s Passive Optical Network (PON).
Easy fixes for modem, ONT, router, and gateway issues
Here are a couple of quick and easy things to try if your modem, ONT, router, or gateway isn’t working properly. Also, see our guides on internet troubleshooting and disconnecting internet for more tips to get your Wi-Fi tip-top shape.
Restart your equipment
Restarting your equipment is always the first step to solving internet problems. This fix is capable of solving a wide range of common internet issues, and it’s super easy.

How to restart a modem, ONT, router, or gateway:
Step 1: Start by unplugging the power cable from your modem, ONT, router, or gateway device.
Step 2: Wait for at least 60 seconds.
Step 3: Plug the power cable back into the modem, ONT, router, or gateway device.
Step 4: Wait for your equipment to reboot. This can take a while—especially if your equipment needs to download and install updates.
Check for damaged or loose cables
It’s easy for damaged or loose cables to go unnoticed until they cause a problem.
First, check for any damaged cables. Look for tears, cuts, harsh kinks, and even chew marks from pets. You can’t always see if a cable is damaged, so when in doubt, replace it if possible. Damaged cabling outside your home will require a technician to fix.
If your cables pass the sniff test, the next step is to check their connections.
For cable internet, make sure the coax cable is screwed on hand-tight to the back of the modem or gateway. Check that the cable is screwed on snug to the wall outlet as well (if available).
For fiber internet, make sure the SFP module is snapped into the PON port on your ONT or fiber gateway (although the Alarm light will glow red if the connection is bad).
If you have DSL internet, the telephone jack should be nice and snug in the RJ11 WAN port on your DSL modem or gateway.
If an Ethernet cable connects a separate modem or ONT to a router, make sure it’s pushed all the way into the Ethernet ports and that the clip isn’t broken, which would allow the cable to fall out. You should hear the connector click as it locks into the Ethernet port.
FAQ about modem, ONT, gateway, and router lights
What do the modem, ONT, router, or gateway lights mean?
Are blinking lights bad?
How do you know if you need a new modem, ONT, router, or gateway?
How do I know what’s going on if there's only one light?
Author -
Kevin Parrish has more than a decade of experience working as a writer, editor, and product tester. He began writing about computer hardware and soon branched out to other devices and services such as networking equipment, phones and tablets, game consoles, and other internet-connected devices. His work has appeared in Tom’s Hardware, Tom's Guide, Maximum PC, Digital Trends, Android Authority, How-To Geek, Lifewire, and others. At HighSpeedInternet.com, he focuses on network equipment testing and review.
Editor - Jessica Brooksby
Jessica loves bringing her passion for the written word and her love of tech into one space at HighSpeedInternet.com. She works with the team’s writers to revise strong, user-focused content so every reader can find the tech that works for them. Jessica has a bachelor’s degree in English from Utah Valley University and seven years of creative and editorial experience. Outside of work, she spends her time gaming, reading, painting, and buying an excessive amount of Legend of Zelda merchandise.







